singleflight应用在什么场景#
singleflight主要应用在高并发场景下,通过对相同请求进行阻塞,减少实际业务方法执行次数,减少依赖服务压力,实际应用场景主要为防止缓存击穿,在接收到请求时,查询redis缓存或查询DB返回结果之前,对后续相同请求进行阻塞,待查询结果返回后被阻塞的n个请求使用相同的返回结果。适用于只读场景。
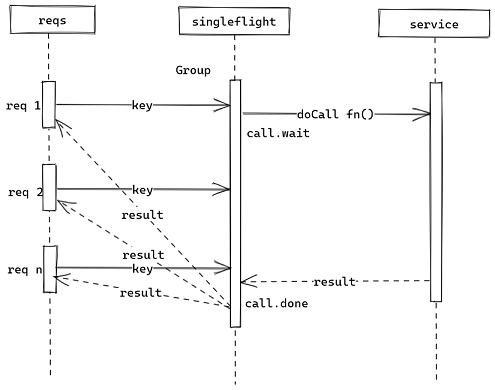
缺点:如果实际业务出错,那么被阻塞的请求也是返回错误,可以创建一个协程每隔一段时间执行Forget(key)来方式业务出错影响太多的请求
代码示例#
package main
import (
"fmt"
"time"
"golang.org/x/sync/singleflight"
)
func main() {
var singleSetCache singleflight.Group
getAndSetCache := func(requestID int, key string) (int64, error) {
value, _, shared := singleSetCache.Do(key, func() (ret interface{}, err error) {
// 此处为实际调用的业务方法,如查询redis缓存,查询DB等
fmt.Printf("requestID: %d doCall...\n", requestID)
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 10) // 模拟doCall耗时,方便其他请求被阻塞
return time.Now().UnixNano(), nil
})
fmt.Printf("requestID: %d, result: %v, shared: %v\n", requestID, value, shared)
return value.(int64), nil
}
key := "demo"
for i := 1; i < 10; i++ { //模拟多个协程同时请求
go func(requestID int) {
_, _ = getAndSetCache(requestID, key)
}(i)
time.Sleep(time.Millisecond * 3) // 每隔3毫秒一个请求
}
time.Sleep(time.Second * 5)
}
/* 输出如下,10个请求,实际只执行了3次doCall, shared表示doCall的结果有没有被其他请求复用
requestID: 1 doCall...
requestID: 1, result: 1685003078081816700, shared: true
requestID: 2, result: 1685003078081816700, shared: true
requestID: 3, result: 1685003078081816700, shared: true
requestID: 4 doCall...
requestID: 4, result: 1685003078093745900, shared: true
requestID: 5, result: 1685003078093745900, shared: true
requestID: 6, result: 1685003078093745900, shared: true
requestID: 7, result: 1685003078093745900, shared: true
requestID: 8 doCall...
requestID: 8, result: 1685003078107540000, shared: true
requestID: 9, result: 1685003078107540000, shared: true
*/
源码解读#
// Group represents a class of work and forms a namespace in
// which units of work can be executed with duplicate suppression.
type Group struct {
mu sync.Mutex // 锁
m map[string]*call // 懒加载
}
// call is an in-flight or completed singleflight.Do call
type call struct {
wg sync.WaitGroup
// 实际业务返回结果, 即Do()方法中fn参数返回的结果
// 以下字段在WaitGroup Done()之前,只写入一次,Done()之后只读
val interface{}
err error
// These fields are read and written with the singleflight
// mutex held before the WaitGroup is done, and are read but
// not written after the WaitGroup is done.
dups int
chans []chan<- Result
}
// 执行fn(),指定key只会执行一次fn()
// 相同key请求到达时,等待首次fn()方法调用,fn()完成之后,复用该结果
func (g *Group) Do(key string, fn func() (interface{}, error)) (v interface{}, err error, shared bool) {
g.mu.Lock()
if g.m == nil {
g.m = make(map[string]*call)
}
// 已经有 in-flight call,则阻塞住,等待原始请求完成
if c, ok := g.m[key]; ok {
c.dups++ // 用于标识call有没有被复用
g.mu.Unlock()
c.wg.Wait()
if e, ok := c.err.(*panicError); ok {
panic(e)
} else if c.err == errGoexit {
runtime.Goexit()
}
return c.val, c.err, true
}
c := new(call)
c.wg.Add(1)
g.m[key] = c
g.mu.Unlock()
g.doCall(c, key, fn)
return c.val, c.err, c.dups > 0
}
// doCall handles the single call for a key.
func (g *Group) doCall(c *call, key string, fn func() (interface{}, error)) {
normalReturn := false
recovered := false
// use double-defer to distinguish panic from runtime.Goexit,
// more details see https://golang.org/cl/134395
defer func() {
// the given function invoked runtime.Goexit
if !normalReturn && !recovered {
c.err = errGoexit // 将err置为goexit
}
g.mu.Lock()
defer g.mu.Unlock()
c.wg.Done()
if g.m[key] == c { // 请求完成,释放key,为什么加这个条件判断不太明白
delete(g.m, key)
}
if e, ok := c.err.(*panicError); ok {
// In order to prevent the waiting channels from being blocked forever,
// needs to ensure that this panic cannot be recovered.
if len(c.chans) > 0 {
go panic(e)
select {} // Keep this goroutine around so that it will appear in the crash dump.
} else {
panic(e)
}
} else if c.err == errGoexit {
// Already in the process of goexit, no need to call again
} else {
// Normal return
for _, ch := range c.chans {
ch <- Result{c.val, c.err, c.dups > 0}
}
}
}()
func() {
defer func() {
if !normalReturn {
// Ideally, we would wait to take a stack trace until we've determined
// whether this is a panic or a runtime.Goexit.
//
// Unfortunately, the only way we can distinguish the two is to see
// whether the recover stopped the goroutine from terminating, and by
// the time we know that, the part of the stack trace relevant to the
// panic has been discarded.
if r := recover(); r != nil {
c.err = newPanicError(r)
}
}
}()
c.val, c.err = fn()
normalReturn = true
}()
if !normalReturn {
recovered = true
}
}
// 手动释放key
func (g *Group) Forget(key string) {
g.mu.Lock()
delete(g.m, key)
g.mu.Unlock()
}
